 Data management often includes RAID because users want to be sure that their data they are working with won’t be corrupted, damaged or lost. Redundancy is the key notion when it comes to data production. On the other hand, some users opt and set up their NAS for better performance gains. Nested RAID (hybrid RAID) is the solution for those who seek both performance and redundancy. Although this configuration is less common, it presents a big advantage compared to single RAID configuration. In short, Nested RAID presents a balance between performance and redundancy level array.
Data management often includes RAID because users want to be sure that their data they are working with won’t be corrupted, damaged or lost. Redundancy is the key notion when it comes to data production. On the other hand, some users opt and set up their NAS for better performance gains. Nested RAID (hybrid RAID) is the solution for those who seek both performance and redundancy. Although this configuration is less common, it presents a big advantage compared to single RAID configuration. In short, Nested RAID presents a balance between performance and redundancy level array. Nested RAID: Intro
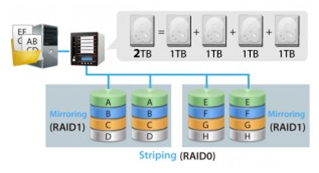
Common Nested RAID configuration are RAID-01 and RAID-10, we’ll use these configurations to go into more details about benefits and requirements of Nested RAID. To elaborate, the number on the left is the lowest RAID and the right number is the top RAID. In most cases, RAID 0 is preferred on top and redundancy is on bottom given that fewer disks are needed to rebuild if disk failure occurs.
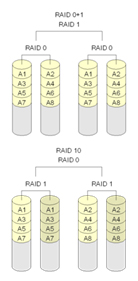 RAID-10 and RAID-01: characteristics
RAID-10 and RAID-01: characteristics
RAID-01
- Redundancy on top of Performance
- Only 50% of storage is usable
- Requires a minimum of four drives
- All disks are required to rebuild, if one disk fails then the whole array will become RAID-0.
RAID-10
- Performance on top of redundancy
- Only 50% of storage is usable
- Requires a minimum of four drives and limited scalability
- Only one disk is involved to rebuild
To review
Nested RAID configurations allow the ability to add enhancements compared to standard RAID levels. This configuration opens doors for NAS users who seek something different than the standard RAID levels but users should be aware that there are some downsides as well.
A concept that comes to mind is, “give a little here, take a little there” since getting more performance or redundancy sacrifices storage space, minimum requirement of disks, or if a disk fails data is lost for RAID-01 to name a few.
To add, Nested RAID is not only restricted to two digits, they can use “RAID-XYZ” if appliance allows. Overall, Nested RAID offers more flexibility to NAS users as some opt for a balance between performance and redundancy instead of a single RAID array.

 O-Sense
O-Sense

.jpg)





.png)

