TESTING METHODOLOGY
As already mentioned plenty of times in the past the performance of Powerline adapters is directly linked to the quality of the buildings electrical grid/wiring so the output speeds from such devices will most probably vary between new and old structures. Still the results recorded when testing Powerline adapters inside the same building should easily point out the best one and so to that end we used the well-known Passmark Performance Test to measure the data transfer rate in wired, wireless and Powerline modes with a fixed (for every test) distance of 15 meters between our Netgear D6300 Gigabit modem/router (we changed from the DGN3500 since after 20 tests we saw no difference in performance with the D6300 between the powerline adapters we have here) and the primary and secondary systems (30m in total between both systems / we make use of CAT7 cables for wired tests). For Wi-Fi capable powerline adapters we left the secondary adapter at the same spot as with the other tests and used it with an 802.11 a/b/g/n/ac compatible Toshiba Qosmio Laptop placed roughly 5 meters away.
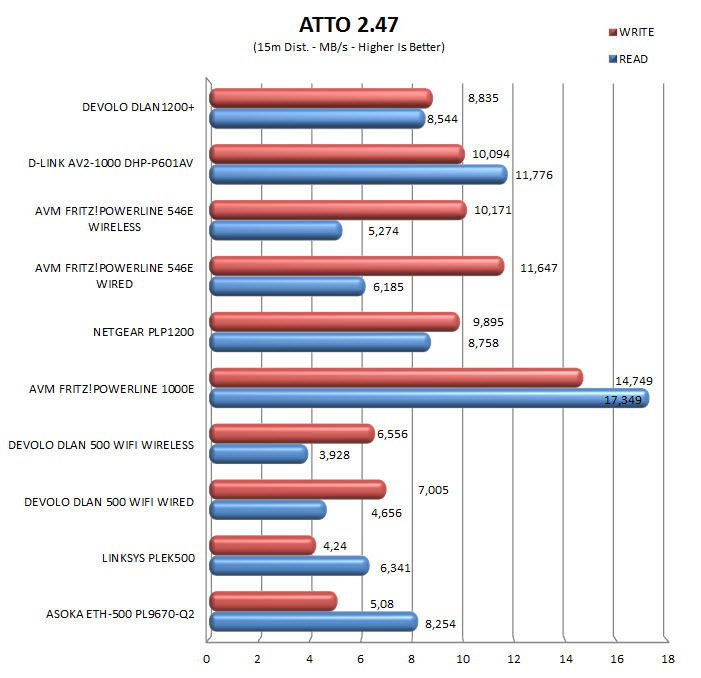
The network data transfer test was set to duration of 40 seconds and was repeated a total of 7 times after which the average numbers were recorded into our charts. As a secondary test we are also using QCheck by Ixia which is considered amongst the top measuring tools of its kind. Tests are performed 7 times at throughput mode with a data size of 1000Kb and in the end the average numbers once again get recorded into our charts. As of February 2015 we also record ATTO results in our charts (256MB total length) after 7 repeats.
TEST RESULTS



 O-Sense
O-Sense

.jpg)





.png)

